Page 257 - 《应用声学》2025年第2期
P. 257
第 44 卷 第 2 期 朱志强等: 超声换能器的超构透镜设计与制备 517
点,这样就能确定声轴上的最远点。再以最远点为 围内。造成该现象的原因主要是 3D 打印透镜材料
基础,将水听器平移至超声换能器表面中心,并将该 的均匀性和几何结构的精度与理论设计有误差,使
点作为声轴的 0 坐标点,以此点为起始点开始测量 得在近场处的声压分布与理论仿真有所偏差。
轴线上各点的声压。水听器的步进为 0.5 mm,这样
3 结论
既能避免平移台移动距离过小而导致的相对误差
偏大,也能够保证测量精度要求。采集到的超声信
该文提出了一种基于超构材料透镜的聚焦超
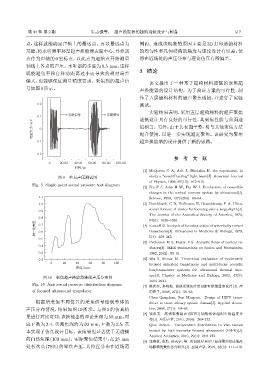
号如图9所示。
声换能器的设计结构。为了验证方案的可行性,制
作了五层超构材料的超声聚焦透镜,并进行了实验
0.2 测试。
实验结果表明,采用五层超构材料的超声聚焦
ԧ࠱ηՂ ᧔ᬷηՂ
0.1 透镜设计具有良好的可行性,其聚焦性能与曲面透
ႃԍܸ࠵/mV 0 镜相当。另外,由于其表面平整,易与其他聚焦方法
配合使用,以进一步实现超近聚焦。该研究为聚焦
-0.1 超声换能器的设计提供了新的思路。
-0.2
参 考 文 献
0 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00
ᫎ/ms
[1] McQueen C A, Arlt J, Dholakia K. An experiment to
图 9 单点声压测试图 study a “nondiffracting” light beam[J]. American Journal
of Physics, 1999, 67(10): 912–915.
Fig. 9 Single point sound pressure test diagram
[2] Fry F J, Ades H W, Fry W J. Production of reversible
changes in the central nervous system by ultrasound[J].
1.1 Science, 1958, 127(3289): 83–84.
1.0 [3] Burckhardt C B, Hoffmann H, Grandchamp P A. Ultra-
sound Axicon: A device for focusing over a large depth[J].
0.9
The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1973,
0.8 54(6): 1628–1630.
ॆʷӑܦԍ 0.7 [4] Kossoff G. Analysis of focusing action of spherically curved
transducers[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 1979,
0.6
0.5 5(4): 359–365.
[5] Patterson M S, Foster F S. Acoustic fields of conical ra-
0.4
diators[J]. IEEE transactions on Sonics and Ultrasonics,
0.3 1982, 29(2): 83–91.
0.2 [6] Wu X, Sherar M. Theoretical evaluation of moderately
0 20 40 60 80 100
focused spherical transducers and multi-focus acoustic
ᡰሏ/mm
lens/transducer systems for ultrasound thermal ther-
apy[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2002, 47(9):
图 10 聚焦超声换能器轴线声压分布图
1603–1621.
Fig. 10 Axis sound pressure distribution diagram
[7] 陈庆春, 孙明灿. 泌尿系统治疗用 HIFU 换能器的设计 [J]. 应
of focused ultrasound transducer 用声学, 2008, 27(1): 59–63.
Chen Qingchun, Sun Mingcan. Design of HIFU trans-
根据所采集不同位置的采集信号绘制整体的 ducer to treat urinary system disease[J]. Applied Acous-
声压分布情况,结果如图 10 所示。与图 5 的仿真结 tics, 2008, 27(1): 59–63.
[8] 钱祖文. 高强聚焦超声 (HIFU) 加热活体组织中的温度分
果进行对比可知,该换能器的理论焦深为58 mm,对
布 [J]. 应用声学, 2010, 29(4): 269–272.
应 F 数为 2.4,实测焦深约为 60 mm,F 数为 2.5,基 Qian Zuwen. Temperature distribution in vivo tissues
本实现了仿真设计目标。该结果也显著优于无透镜 heated by high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU)[J].
Applied Acoustics, 2010, 29(4): 269–272.
的自然焦深(103 mm)。实际聚焦结果中,在25 mm
[9] 张艳秋, 张浩, 孙天宇, 等. 剪切波对 HIFU 经颅聚焦形成温度
处有次高 (78%) 的聚焦声压,其位置分布在近场范 场影响的数值仿真研究 [J]. 应用声学, 2019, 38(3): 411–418.