Page 136 - 201901
P. 136
132 2019 年 1 月
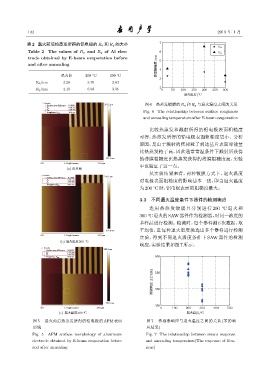
表 2 退火前后热蒸发所得的铝电极的 R a 和 R q 的大小 7
R a
Table 2 The values of R a and R q of Al elec- 6 R q
᛫᭧ዤጀए/nm 4
trode obtained by E-beam evaporation before 5
and after annealing
退火前 200 C 300 C
◦
◦
3
R a/nm 3.28 3.75 2.63
R q /nm 4.10 6.58 3.35 2 0 50 100 150 200 250 300
ᤞ༢ພए/C
Results 287.2 nm 图 6 热蒸发镀膜的 R a 和 R q 与退火温度之间的关系
Surface area difference 0.592%
R q 4.10 nm
R a 3.28 nm
Roughness R max 26.8 nm Fig. 6 The relationship between surface roughness
and annealing temperature after E-beam evaporation
比较热蒸发和溅射所得的铝电极表面粗糙度
可得,热蒸发所得的铝电极表面粗糙度更小。分析
原因,是由于溅射的靶材粒子到达基片表面时能量
比热蒸发粒子高,因此通常常温条件下溅射所获得
的薄膜粗糙度比热蒸发获得的薄膜粗糙度高,实验
-253.2 nm
0.0 1: Height sensor 35.0 µm
中也验证了这一点。
(a) ᤞ༢Ғ
从实验结果来看,两种镀膜方式下,退火温度
Results 232.3 nm
Surface area difference 0.558%
R q 6.58 nm 对电极表面粗糙度的影响基本一致,即当退火温度
R a 3.75 nm
Roughness R max 94.1 nm
为200 C时,铝电极表面的粗糙度最大。
◦
3.2 不同退火温度条件下器件的检测响应
选用热蒸发镀膜且分别进行 200 C 退火和
◦
300 C退火的SAW器件作为检测器,对同一浓度的
◦
苯样品进行检测。检测时,每个器件测6 次数据,取
平均值,且每种退火温度挑选出多个器件进行检测
-219.0 nm
0.0 1: Height sensor 35.0 µm
实验,得到不同退火温度条件下 SAW 器件的检测
(b) ᤞ༢ພए200 C
响应,实验结果如图7所示。
Results
Surface area difference 0.365% 289.9 nm
R q 3.35 nm
R a 2.63 nm
Roughness R max 24.6 nm 650
ត־ऄ Df⊳kHz 550
450
-273.5 nm
350
0.0 1: Height sensor 35.0 µm 0 100 200 300 400 500
(c) ᤞ༢ພए300 C ᤞ༢ພए/C
图 5 退火前后热蒸发所得的铝电极的 AFM 表面 图 7 传感器响应与退火温度之间的关系 (苯的响
形貌 应结果)
Fig. 5 AFM surface morphology of aluminum Fig. 7 The relationship between sensor response
electrode obtained by E-beam evaporation before and annealing temperature(The response of Ben-
and after annealing zene)