Page 95 - 201901
P. 95
第 38 卷 第 1 期 李楠等: 一种基于虚拟传感的无需误差传声器的自适应有源降噪方法 91
0.05
ηՂࣨए -0.05 0 ጟᤰ᥋үԧၷ
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
ᫎ/s
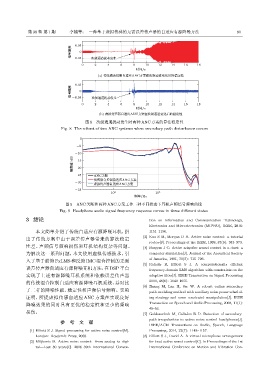
(a) ͜ፒຉՌ҄ᒭᤠऄANCவವښጟᤰ᥋ԫӑՑᄊሷࠀভ
0.05
ηՂࣨए -0.05 0 ጟᤰ᥋үԧၷ
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
ᫎ/s
(b) ᘿલ͜ܦ٨ᒭᤠऄANCவವښጟᤰ᥋ԫӑՑᄊሷࠀভ
图 8 次级通道扰动发生时两种 ANC 方案的算法稳定性
Fig. 8 The robust of two ANC systems when secondary path disturbance occurs
0
-5
-10
ࣨए៨/dB -15
-20
-25 ANCТல
͜ፒຉՌ҄ᒭᤠऄANCவವ
-30
ᘿલ͜ܦ٨ᒭᤠऄANCவವ
-35
10 2 10 3
ᮠဋ/Hz
图 9 ANC 关断和两种 ANC 方案工作三种不同状态下耳机声频信号频响曲线
Fig. 9 Headphone audio signal frequency response curves in three different states
3 结论 tion on Information and Communication Technology,
Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), IEEE, 2016:
本文简单介绍了传统自适应有源降噪耳机,指 1151–1156.
[3] Kuo S M, Morgan D R. Active noise control: a tutorial
出了传统方案中由于误差传声器带来的算法稳定
review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(6): 943–973.
性差、声频信号频响损伤和耳机结构复杂等问题。 [4] Burgess J C. Active adaptive sound control in a duct: a
为解决这一系列问题,本文使用虚拟传感技术,引 computer simulation[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society
入了基于前馈 FxLMS和反馈IMC混合控制的无需 of America, 1981, 70(3): 715–726.
[5] Rafaely B, Elliott S J. A computationally efficient
误差传声器自适应有源降噪耳机方法,在DSP平台 frequency-domain LMS algorithm with constraints on the
实现了上述有源降噪耳机系统和依赖误差传声器 adaptive filter[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing
的传统混合控制自适应有源降噪耳机系统,并对比 2000, 48(6): 1649–1655.
[6] Zhang M, Lan H, Ser W. A robust online secondary
了二者的降噪性能、稳定性和声频信号频响。实验 path modeling method with auxiliary noise power schedul-
证明,所提虚拟传感自适应 ANC 方案在实现良好 ing strategy and norm constraint manipulation[J]. IEEE
降噪效果的同时具有更优的稳定性和更少的频响 Transaction on Speech and Audio Processing, 2003, 11(1):
45–53.
损伤。 [7] Guldenschuh M, Callafon R D. Detection of secondary-
path irregularities in active noise control headphones[J].
参 考 文 献
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, Language
[1] Elliott S J. Signal processing for active noise control[M]. Processing, 2014, 22(7): 1148–1157.
London: Academic Press, 2000. [8] Elliott S J, David A. A virtual microphone arrangement
[2] Miljkovic D. Active noise control: from analog to digi- for local active sound control[C]. In Proceedings of the l st
tal—Last 80 years[C]. 2016 39th International Conven- International Conference on Motion and Vibration Con-